Infections had occurred in the major cities of Kampala and Jinja, fuelling concerns that the disease could extend well into 2023. In 2019, Uganda experienced an outbreak of the Zaire strain of Ebola.
Head of the UN health agency, Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, congratulated the authorities for their “robust” response to the outbreak, less than four months after the first case of Sudan Ebola virus was confirmed, in central Mubende district.
“Uganda has shown that Ebola can be defeated when the whole system works together, from having an alert system in place, to finding and caring for people affected and their contacts, to gaining the full participation of affected communities in the response,” Tedros said.
Unwelcome visitor
In all, 55 people died and 87 recovered in the latest outbreak, according to WHO, whose Regional Director for Africa, Dr Matshidiso Moeti, noted that no vaccines yet exist to treat the Sudan strain.
“This was one of the most challenging Ebola outbreaks in the past five years,” Dr Moeti said. “But Uganda stayed the course and continuously fine-tuned its response.
“Two months ago, it looked as if Ebola would cast a dark shadow over the country well into 2023…this win starts off the year on a note of great hope for Africa.”
The ‘magic bullet’: Community engagement
The virus is transmitted to people from wild animals and can spread through direct contact with infected people’s blood or other bodily fluids. Symptoms of Ebola – formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever – include fever and vomiting, accompanied by internal and external bleeding.
To stop further transmission of the virus – which was the country’s first encounter with Sudan Ebola virus in a decade – WHO worked with national health teams to explain the threat to at-risk populations and the need for restricted movement in the infection hot-spots of Mubende and Kasanda.
“While we expanded our efforts to put a strong response in place across the nine affected districts, the magic bullet has been our communities who understood the importance of doing what was needed to end the outbreak, and took action,” said Dr Jane Ruth Aceng Acero, Uganda’s Minister of Health.
WHO also helped to track more than 4,000 people who came into contact with people infected with the Ebola virus. Once identified, these contacts were monitored for 21 days, before being given the all-clear.
The last patient was released from care on 30 November when the 42-day countdown to the end of the outbreak began, according to WHO, which noted that the case fatality rate for this outbreak, was 47 per cent.
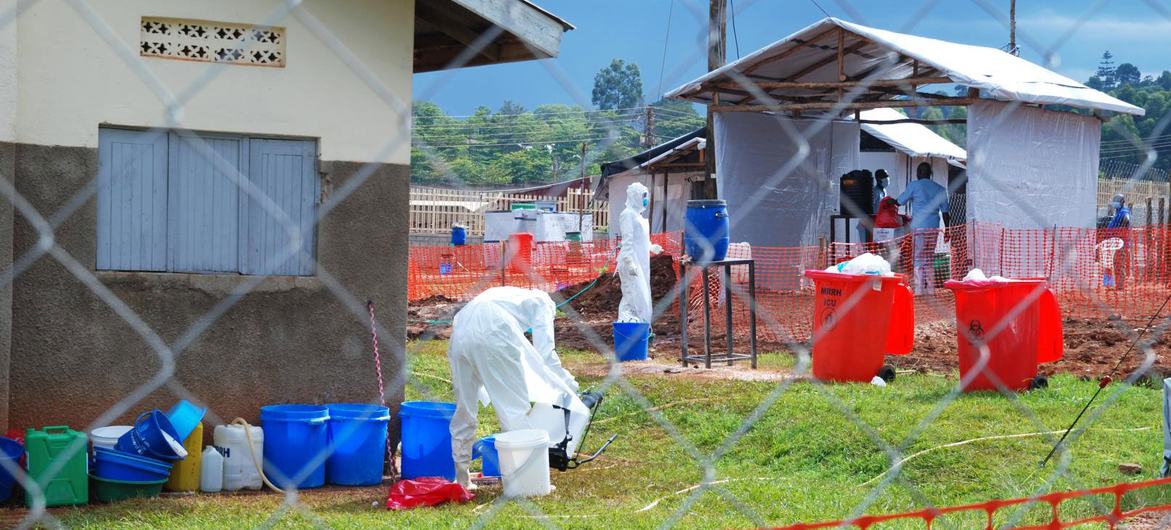

Uganda declares end of Ebola disease outbreak.
Sharing the burden
The UN health agency provided nearly S$ 6.5 million for the initial response and an additional $3 million to support readiness in six neighbouring countries.
Practical support from WHO included deploying experts, providing training in contact tracing, testing and patient care, as well as building isolation and treatment centres and providing laboratory testing kits.
Thanks to these joint efforts, “the processing time for Ebola samples dropped from a few days, to six hours”, WHO said, adding that it had helped to protect frontline health workers by making a steady supply of personal protective equipment available.
Prepared for the next outbreak
The WHO also included working with partners including vaccine developers, researchers, donors and the Ugandan health authorities, to identify candidate therapeutics and vaccines for inclusion in trials.
Three trial vaccines were identified and over 5,000 doses reached Uganda in record time last month, 79 days after the outbreak was declared.
Although no vaccines were deployed this time, the UN agency insisted that the rapid response to the health threat “marks a milestone in the global capacity to respond to rapidly evolving outbreaks and prevent them from becoming larger”.
Sudan Ebola virus is one of six strains of the disease for which there are no approved therapeutics or vaccines. To counter this handicap, WHO explained that Uganda had been able to utilise its long experience in responding to epidemics and “rapidly strengthen critical areas of the response”.